5G and Preparing for 6G

5G and Preparing for 6G
by vivienne 10:07am Jan 08, 2025
The rollout of 5G technology marked a pivotal moment in global connectivity, ushering in new standards for speed, latency, and device density. As industries and consumers adapt to the benefits of 5G, the next frontier—6G—is already under exploration. While 5G continues to impact sectors such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and augmented reality, the anticipated capabilities of 6G promise to redefine the boundaries of innovation even further. This transition is about more than speed; it’s about a fundamentally new level of interconnectedness, intelligence, and responsiveness.
Understanding 5G and Its Impact
5G, or the fifth generation of wireless technology, is distinguished by its high speeds, low latency, and the ability to support a dense network of devices. Compared to its predecessor, 4G, 5G can deliver speeds up to 100 times faster with latency as low as one millisecond. These capabilities have enabled advancements across various domains:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): 5G’s fast speeds and high bandwidth allow for superior video streaming, cloud gaming, and high-quality video calls, transforming the way people consume and share content.
Massive-Machine-Type Communications (mMTC): With the capacity to handle up to one million devices per square kilometer, 5G can support dense IoT ecosystems. This is critical for smart cities, where interconnected sensors, cameras, and vehicles rely on seamless communication.
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC): 5G’s low latency is crucial for real-time applications like autonomous driving, robotic surgery, and critical infrastructure management. Faster response times reduce risks and enhance precision in these high-stakes scenarios.
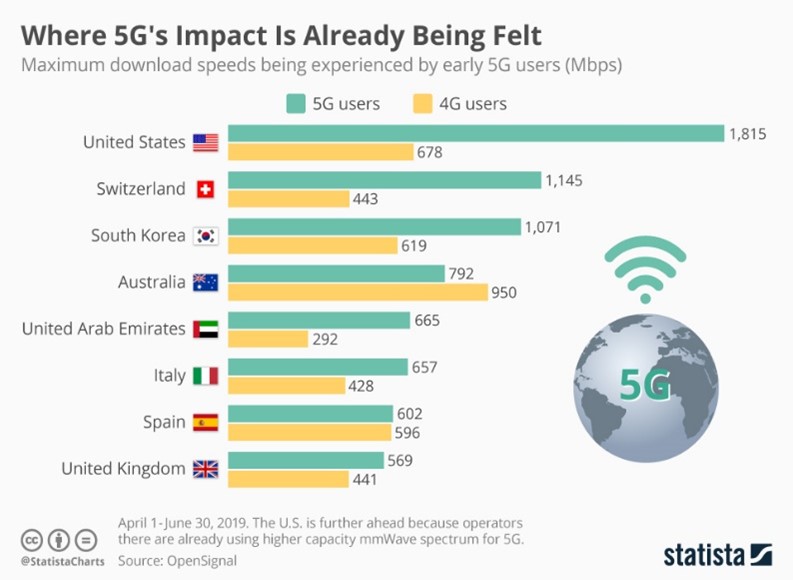
Challenges in Implementing 5G
While 5G offers transformative potential, its implementation comes with challenges:
· Infrastructure Investment: Building a 5G network requires substantial infrastructure, including new base stations and extensive fiber optic cabling. This can be costly, particularly in rural or hard-to-reach areas.
· Spectrum Limitations: 5G uses a variety of frequency bands, including millimeter waves that offer high speeds but have limited range and difficulty penetrating obstacles like walls or buildings. This necessitates careful planning to ensure consistent coverage.
· Device Compatibility: Not all devices are compatible with 5G, and the technology requires new, 5G-enabled smartphones and IoT devices, which can limit accessibility in the early stages of deployment.
What is 6G?
6G, or the sixth generation of wireless technology, is still in the early research phase, with commercialization expected around 2030. While exact specifications are yet to be determined, researchers and technology firms are exploring a range of capabilities that 6G could bring:
1. Speeds Beyond Imagination: 6G is expected to deliver speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G, potentially reaching up to 1 terabit per second. This would enable instant downloads of large datasets, revolutionizing industries like entertainment, healthcare, and research.
2. Sub-Millisecond Latency: With latency potentially dropping below one millisecond, 6G would enable true real-time interactions, critical for applications like telepresence, holographic communication, and high-precision robotics.
3. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI): 6G will likely be AI-native, meaning it will leverage AI to optimize network performance, manage traffic, and deliver personalized experiences. AI-powered 6G could enable context-aware applications that adapt to users’ needs dynamically.
4. Extreme Connectivity for IoT: 6G aims to support a much larger number of devices per square kilometer than 5G, accommodating advanced IoT networks. With these capabilities, smart cities, connected industries, and smart homes could operate with seamless data flow and interoperability.
5. New Spectrum Bands: 6G may extend into the terahertz frequency range (THz), allowing for unprecedented data rates and bandwidth. However, the development of this spectrum will involve overcoming significant challenges in terms of propagation and energy efficiency. 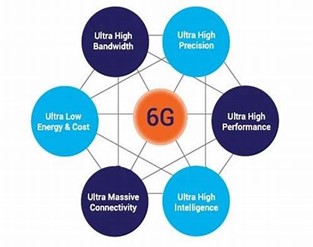
Preparing for the Transition to 6G
While 6G is still a decade away, industries and governments are already taking steps to prepare:
· Early Research and Development: Organizations such as the Next G Alliance, a coalition of industry leaders and researchers, are conducting early R&D to set the technical foundations for 6G, focusing on spectrum allocation, standards, and regulatory considerations.
· Investment in AI and Edge Computing: As 6G is expected to be AI-driven, investment in AI and edge computing infrastructure will be critical. These technologies will play a central role in managing network complexity, optimizing resource allocation, and delivering the low-latency, context-aware experiences that 6G promises.
· Focus on Sustainable Design: Given the energy demands of high-speed, high-capacity networks, sustainability will be a key consideration. Researchers are exploring ways to make 6G networks more energy-efficient, which will be critical in reducing the environmental impact of widespread connectivity.
· Global Collaboration for Standards and Security: Developing global standards and security protocols for 6G is essential to ensure interoperability, reliability, and data privacy. Collaboration between governments, technology companies, and research institutions will be crucial in establishing a secure and standardized 6G framework. 
Conclusion
5G has already set a new standard for connectivity, creating unprecedented opportunities for innovation and enabling transformative applications across industries. As we look ahead, 6G promises to further enhance connectivity, making possible experiences that were once the realm of science fiction. However, realizing this potential will require coordinated efforts in research, infrastructure development, and regulatory frameworks.
By preparing for 6G today, businesses and governments can position themselves at the forefront of the next wave of digital transformation, unlocking a future of hyper-connectivity, advanced AI, and real-time data intelligence that will reshape our world.






