Cyber Warfare and International Security

Cyber Warfare and International Security
by vivienne 12:22pm Jan 08, 2025

Introduction
Define Cyber Warfare: Start with a clear, concise definition of cyber warfare, explaining that it involves attacks on information systems, networks, and infrastructure by states, non-state actors, or individuals with a view to inflict harm, gain intelligence, or undermine the stability of targeted nations.
Significance for International Security: Mention why cyber warfare has become a top concern for international security. The digital interconnectivity of systems means attacks can transcend borders, affecting military, economic, and civil infrastructures globally.
Growing Threat: Point out recent trends showing an increase in the scale, sophistication, and frequency of cyber attacks targeting critical infrastructure worldwide. Mention high-profile incidents (e.g., the Stuxnet worm, SolarWinds, or recent ransomware attacks) as examples.

The Evolution of Cyber Warfare
Historical Background: Describe the beginnings of cyber conflict, where hacking and espionage evolved from relatively simple operations to state-sponsored cyber attacks.
Notable Examples: Provide a brief analysis of some famous incidents, like the 2007 cyber attacks on Estonia or the 2014 Sony Pictures hack, to illustrate how cyber warfare tactics have become more advanced.
Militarization of Cyberspace: Discuss how militaries worldwide have integrated cyber strategies into their defense and attack capabilities, including the creation of dedicated cyber units and operations.
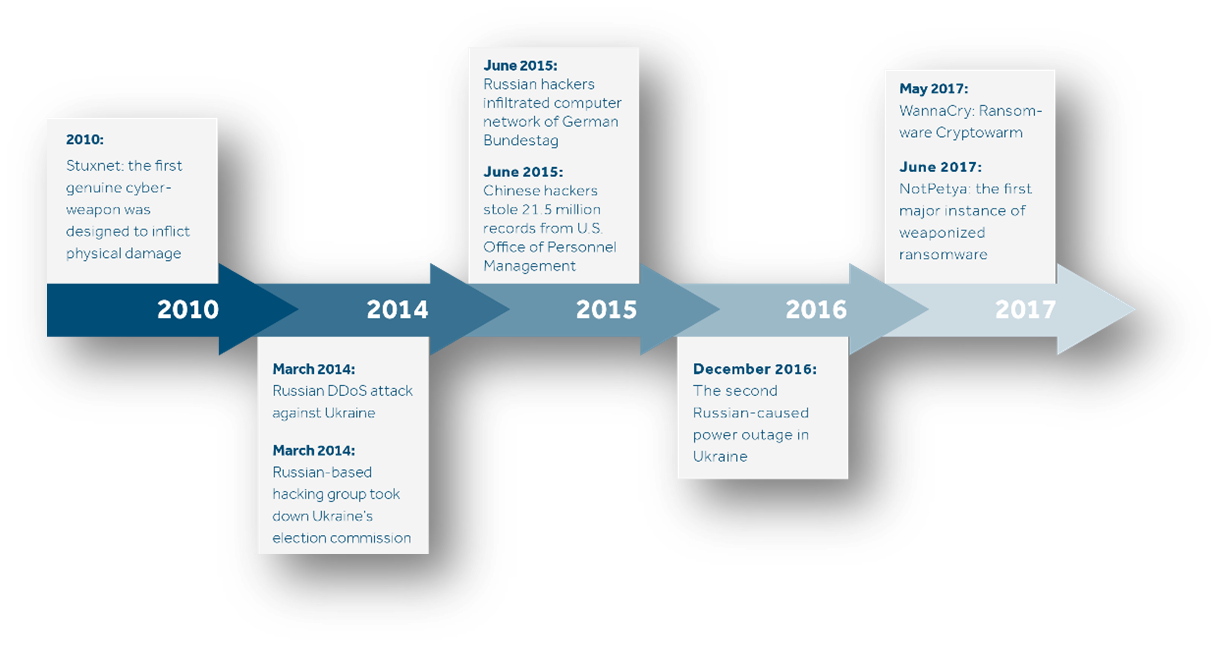
Current Threat Landscape
State-Sponsored Attacks: Explain the role of states in cyber warfare, with nations like the U.S., China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea heavily investing in cyber capabilities for defense and offense. Emphasize motivations, such as espionage, disruption, and influencing political outcomes.
Non-State Actors and Cyberterrorism: Include non-state actors such as cybercriminals, hacktivists, and terrorist organizations, which can independently or in coordination with states, launch cyber attacks for various purposes.
Critical Infrastructure: Emphasize the importance of protecting critical infrastructure (energy grids, transportation, financial systems) and how cyber attacks can lead to economic loss, panic, or even fatalities.

Implications for International Security
Escalation and Misunderstanding: Describe how cyber attacks can escalate into military conflicts if misinterpreted. The anonymity of cyber space complicates attribution, making it challenging to hold perpetrators accountable.
Destabilization of Global Order: Cyber warfare disrupts the balance of power by allowing less wealthy nations to engage in asymmetrical warfare, threatening international stability.
Cyber Deterrence: Discuss how traditional deterrence (nuclear or conventional military) strategies are complex to apply in cyberspace, where it's difficult to attribute attacks and gauge responses.
Legal and Ethical Issues
International Law and Cyber Warfare: Explain that international laws like the Geneva Conventions don’t fully apply to cyberspace, creating challenges in regulating cyber warfare. Mention efforts by the UN and other entities to create frameworks, such as the Tallinn Manual.
Privacy and Civil Liberties: Address ethical concerns, such as the potential for surveillance or control of information, and the consequences on freedom of expression and privacy.
Challenges of Attribution and Accountability: Explain how the difficulty in attributing attacks complicates holding actors accountable and enforcing laws.

Efforts in Cyber Diplomacy and Security Cooperation
Bilateral and Multilateral Agreements: Provide examples of international efforts like the U.S.-China Cyber Agreement or NATO’s cyber defense initiatives.
UN and Cyber Norms: Mention initiatives by the UN Group of Governmental Experts (UN GGE) and other groups working to develop norms for responsible state behavior in cyberspace.
Cyber Security Alliances: Discuss alliances like the NATO Cooperative Cyber Defence Centre of Excellence and the European Union’s Cybersecurity Strategy to highlight collective security efforts.
Challenges Ahead and the Future of Cyber Warfare
Technological Advancements: Discuss how advancements in AI, quantum computing, and IoT may escalate cyber warfare by enabling more complex attacks.
Policy and Preparedness: Emphasize the importance of developing robust cybersecurity policies and training across sectors to reduce vulnerabilities.
Balance of Security and Freedom: Highlight the balancing act needed between ensuring security and protecting individual freedoms and democratic values in the age of cyber conflict.
Conclusion
Call for Global Cooperation: Reinforce that international cooperation, clear legal frameworks, and a strong emphasis on cybersecurity are essential to countering the threats posed by cyber warfare. Adapting to Evolving Threats: Conclude by stressing that as the nature of warfare continues to evolve in the digital domain, governments, industries, and citizens alike must adapt, staying vigilant and prepared for the challenges posed by cyber threats to global security.






