Can AI help create fully autonomous microgrids for sustainable energy management?

Can AI help create fully autonomous microgrids for sustainable energy management?
by Maximilian 10:33am Jan 24, 2025
Yes, AI can play a crucial role in creating fully autonomous microgrids for sustainable energy management. Autonomous microgrids are small-scale, self-sufficient energy systems that operate independently or in coordination with the main grid. They integrate renewable energy sources, storage, and advanced control systems. AI enables their efficient and sustainable operation through automation, optimization, and real-time decision-making.
Key Roles of AI in Autonomous Microgrids
1. Real-Time Energy Management
Demand-Supply Balancing: AI algorithms continuously monitor energy demand and generation, dynamically balancing the two to ensure reliability.
Energy Prioritization: During shortages, AI allocates energy based on pre-defined priorities, ensuring critical systems remain operational.
2. Renewable Energy Integration
Forecasting: AI predicts renewable energy production based on weather and environmental data, optimizing the use of resources like solar and wind.
Mitigating Variability: AI dynamically adjusts storage and load to address the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Equipment Monitoring: AI analyzes sensor data to detect wear and tear on components like inverters, batteries, and generators.
Failure Prevention: Predictive models anticipate potential failures, enabling preemptive maintenance and reducing downtime.

4. Optimizing Energy Storage
Battery Management Systems (BMS): AI ensures efficient charging and discharging cycles, extending battery life and optimizing storage utilization.
Energy Arbitrage: AI identifies the best times to store energy (when demand and prices are low) and release it (when demand and prices are high).
5. Autonomous Grid Operations
Island Mode Transition: AI enables seamless transitions between grid-connected and island modes, ensuring uninterrupted energy supply during outages.
Self-Healing: AI detects faults in the microgrid and reroutes power or isolates faulty components to minimize disruptions.
6. Demand Response and Load Management
Smart Appliances: AI integrates with IoT-enabled devices, automating energy use based on grid conditions and consumer preferences.
Dynamic Pricing: AI helps implement demand-response programs, incentivizing users to shift consumption to off-peak times.
7. Integration with Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): AI optimizes the use of EVs as mobile energy storage, charging them during low-demand periods and discharging to the grid during high demand.
Charging Management: AI schedules EV charging to minimize strain on the microgrid and maximize use of renewable energy.
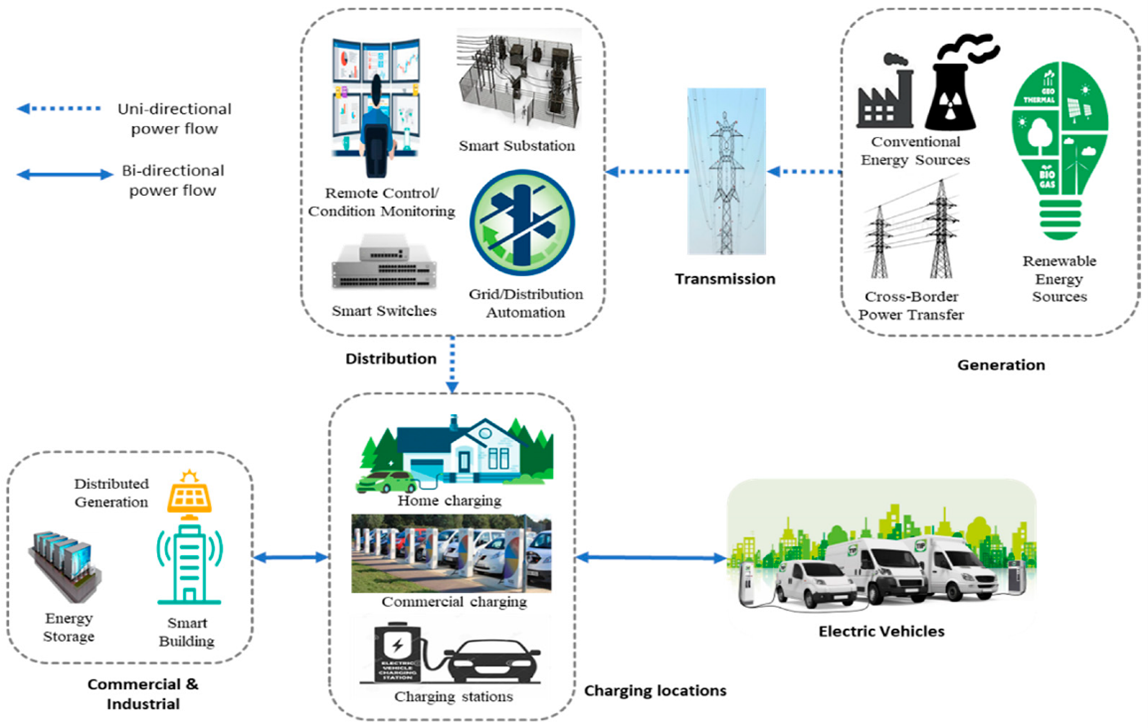
8. Economic Optimization
Cost Reduction: AI minimizes operational costs by optimizing energy generation, storage, and usage.
Revenue Maximization: AI identifies opportunities to sell excess energy to the main grid or neighboring microgrids.
9. Decentralized Energy Trading
Peer-to-Peer Energy Markets: AI enables microgrids to trade energy with each other through blockchain-backed platforms.
Market Forecasting: AI predicts energy prices and demand, ensuring optimal trading decisions.
10. Scalability and Adaptability
Scalable Architecture: AI can manage the complexity of expanding microgrids, integrating additional generation or storage capacity.
Learning Capabilities: Machine learning models improve over time, adapting to changes in consumption patterns, weather, or grid conditions.
Benefits of AI-Driven Autonomous Microgrids
Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on the main grid by efficiently utilizing local resources.
Increased Reliability: Ensures uninterrupted power supply, even during grid outages.
Cost Efficiency: Lowers energy costs through optimized operations and renewable integration.
Environmental Sustainability: Maximizes the use of renewable energy, reducing carbon footprints.
Community Resilience: Strengthens energy resilience for communities, particularly in remote or disaster-prone areas.

Challenges and Solutions
Data Complexity: Managing diverse data from multiple sources can be challenging.
Solution: Use AI-powered edge computing to process data locally and in real-time.
Cybersecurity Risks: Autonomous systems can be vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Solution: Implement robust AI-driven cybersecurity protocols, such as anomaly detection and encrypted communications.
Initial Costs: High upfront costs for AI and infrastructure.
Solution: Leverage AI to reduce long-term operational costs, making the investment viable over time.
By integrating AI into microgrid management, we can create highly efficient, resilient, and sustainable energy systems capable of meeting modern energy challenges while advancing the transition to clean energy.






