What role does AI play in predictive maintenance for industrial equipment?

What role does AI play in predictive maintenance for industrial equipment?
by Maximilian 12:12pm Jan 25, 2025

AI plays a transformative role in predictive maintenance for industrial equipment by leveraging data-driven insights to anticipate and address issues before they lead to failures. This reduces downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and enhances operational efficiency. Here's a breakdown of its contributions:
1. Real-Time Data Collection and Monitoring
AI systems continuously collect and analyze data from various sources, such as:
IoT Sensors: Measure parameters like temperature, vibration, pressure, and noise.
SCADA Systems: Provide operational data from industrial processes.
Historical Maintenance Records: Offer insights into past failures and maintenance activities.
By processing this data in real time, AI detects patterns that indicate potential equipment issues.

2. Fault Detection and Diagnosis
AI algorithms can identify early warning signs of faults, often undetectable by human operators:
Anomaly Detection: Machine learning models recognize deviations from normal operating behavior.
Root Cause Analysis: AI pinpoints the underlying causes of anomalies, guiding maintenance teams to the specific issue.
3. Predictive Analytics
Using historical and real-time data, AI predicts when equipment components are likely to fail:
Time-to-Failure Models: Estimate the remaining useful life (RUL) of critical components.
Event Forecasting: Predicts specific failure events, enabling timely interventions.
4. Optimized Maintenance Scheduling
AI helps organizations move from reactive to proactive maintenance:
Dynamic Scheduling: Prioritizes maintenance tasks based on urgency and equipment criticality.
Cost Optimization: Reduces unnecessary preventive maintenance and avoids costly unplanned repairs.
5. Machine Learning Techniques in Predictive Maintenance
AI leverages various machine learning techniques:
Supervised Learning: Models trained on labeled data predict failure types or maintenance needs.
Unsupervised Learning: Clusters operational data to identify abnormal patterns without prior labels.
Deep Learning: Analyzes complex datasets, such as time-series sensor readings or image data from inspections.
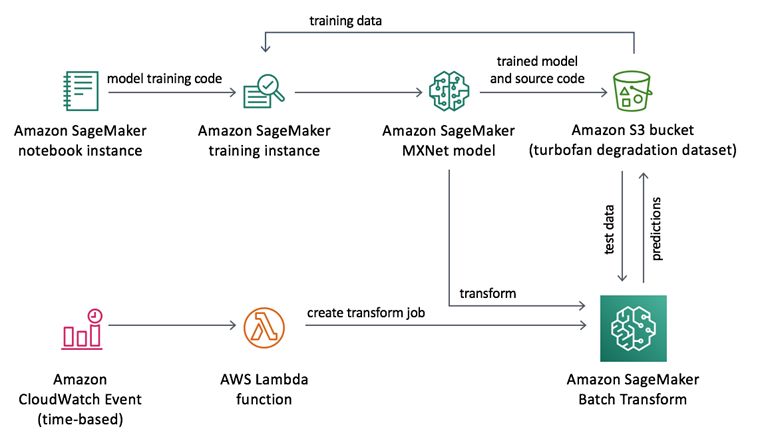
6. Case Studies and Applications
Oil & Gas Industry: AI predicts pipeline corrosion and equipment wear, preventing catastrophic failures.
Manufacturing: Detects anomalies in rotating machinery, such as motors or compressors, to avoid production stoppages.
Aviation: Monitors aircraft engines for early signs of wear, improving safety and reducing unscheduled maintenance.
Energy Sector: Optimizes wind turbine and solar panel maintenance to maximize energy production.
7. Enhanced Accuracy with Digital Twins
Digital twins, virtual replicas of physical equipment, simulate performance under various conditions:
AI-driven models compare real-time data with the digital twin to identify discrepancies.
Predictive simulations test "what-if" scenarios, helping to refine maintenance strategies.

8. Challenges in AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance
Data Quality: Insufficient or noisy data can reduce prediction accuracy.
Integration Complexity: Legacy systems may need upgrades to support AI.
High Initial Investment: Implementing AI solutions involves upfront costs, although savings accrue over time.
Workforce Adaptation: Requires training personnel to interpret AI insights and implement recommendations.
By enabling smarter, data-driven maintenance strategies, AI ensures higher equipment reliability, longer asset lifespans, and more cost-effective operations across industries.






