Strategies for integrating circularity into global supply chains

Strategies for integrating circularity into global supply chains
by vivienne 10:49am Jan 03, 2025
Integrating circularity into global supply chains involves adopting strategies that reduce waste, maximize resource use, and promote sustainability throughout the lifecycle of products and materials. Here are key strategies for integrating circularity into global supply chains:
1. Design for Circularity
Product Design for Longevity: Focus on designing products that are durable, easy to repair, and upgradeable, reducing the need for frequent replacement.
Modular Design: Design products in modular components to facilitate easier disassembly, repair, or reuse of parts at the end of the product's lifecycle.
Use of Recyclable Materials: Ensure that products are made from materials that can be easily recycled or upcycled, reducing dependence on virgin resources.
2. Supplier Engagement and Collaboration
Sustainable Sourcing: Collaborate with suppliers to source raw materials sustainably, prioritize renewable resources, and ensure ethical production processes.
Circular Supplier Partnerships: Build partnerships with suppliers who are also adopting circular practices, such as those who recycle materials, implement energy-efficient practices, or offer repairable components.
3. Reverse Logistics and Take-Back Systems
Product Take-Back Programs: Develop programs where customers return used products or materials at the end of their lifecycle for reuse, refurbishment, or recycling.
Closed-Loop Systems: Establish a closed-loop supply chain where products are returned, remanufactured, and put back into circulation, reducing the need for new raw materials.
4. Data and Technology Integration
Track and Trace Systems: Use digital technologies like IoT and blockchain to track materials and products throughout the supply chain. This can help ensure traceability of raw materials and aid in the efficient management of resources.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverage data analytics to optimize inventory management, predict product demand, and identify opportunities for resource optimization.
Automation and AI for Efficiency: Use AI and automation to streamline production processes, reduce waste, and enhance material flow efficiency.

5. Circular Business Models
Product-as-a-Service (PaaS): Shift from a model where customers own products to one where they lease or pay for the use of products, facilitating product take-back and reuse.
Remanufacturing and Refurbishment: Establish processes for remanufacturing and refurbishing used products or components, rather than discarding them. This extends the lifecycle of products and reduces waste.
6. Circular Economy Standards and Certifications
Adopt Circular Economy Standards: Implement global or industry-specific standards for circularity that ensure products and processes meet sustainability criteria. Examples include Cradle to Cradle certification or ISO 14001.
Third-Party Auditing: Use third-party audits to verify circularity practices, such as waste reduction, use of sustainable materials, and environmental performance.
7. Material Recovery and Recycling
Design for Disassembly: Create products that are easy to disassemble, allowing materials to be recovered, recycled, and reused efficiently.
Advanced Recycling Technologies: Invest in cutting-edge recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling, which allows more materials to be recycled in a closed-loop manner, especially those that are difficult to recycle using traditional methods.
8. Supply Chain Transparency and Consumer Engagement
Transparency and Reporting: Provide transparent reporting on circular practices and sustainability efforts to stakeholders and consumers. This includes carbon footprint analysis, waste reduction initiatives, and supply chain sustainability.
Educate Consumers: Engage consumers in the circular economy by informing them about the benefits of returning products, repairing them, or choosing sustainable options. Offer incentives for sustainable consumer behavior.
9. Incentivizing Circular Innovations
R&D Investment: Invest in research and development to explore new materials, recycling technologies, and innovative business models that support circularity.
-
Innovation Hubs and Startups: Collaborate with startups and innovation hubs that focus on circular economy solutions, such as creating biodegradable packaging or developing alternative materials from waste.
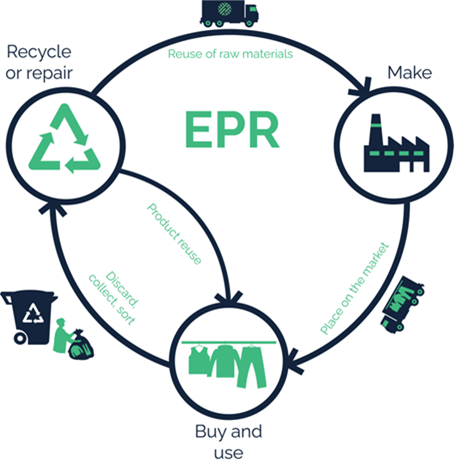
10. Collaborative Policy Advocacy
Advocating for Circular Economy Policies: Collaborate with governments and industry groups to create favorable policies and regulations that promote circular practices, such as extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws or tax incentives for recycling.
By integrating these strategies, companies can contribute to a circular economy, reduce waste, and drive more sustainable practices throughout their global supply chains.






