Cybersecurity threats and how businesses can prepare

Cybersecurity threats and how businesses can prepare
by vivienne 06:24pm Jan 03, 2025

Cybersecurity threats are a significant risk to businesses of all sizes and sectors. These threats can result in financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. 
Below are some common types of cybersecurity threats and how businesses can prepare for them:
1. Phishing Attacks
What it is: Phishing is when attackers impersonate legitimate entities (e.g., banks, trusted colleagues, or government agencies) to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal details.
How businesses can prepare:
Employee Training: Educate employees on how to recognize phishing emails and messages.
Email Filters: Use advanced email filtering software to identify and block suspicious emails.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to reduce the impact of stolen credentials.
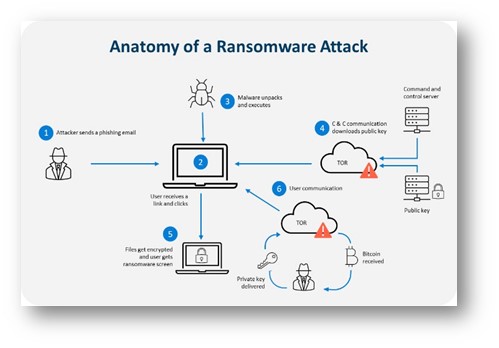
2. Ransomware
What it is: Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts a company’s data and demands payment (usually in cryptocurrency) for decryption keys.
How businesses can prepare:
Regular Backups: Regularly back up important data and store backups offline to avoid ransomware targeting them.
Network Segmentation: Segment critical systems and data to limit the spread of an attack.
Security Patches: Keep all systems and software up-to-date with the latest security patches.
3. Insider Threats
What it is: Insider threats involve current or former employees, contractors, or other trusted individuals who misuse their access to company systems to steal data, sabotage operations, or cause other damage.
How businesses can prepare:
Access Controls: Implement strict access controls, ensuring employees only have access to the information they need for their jobs.
Monitoring: Regularly monitor employee activity on corporate networks and systems.
Exit Procedures: Have clear procedures for offboarding employees and ensuring they no longer have access to sensitive information.
4. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
What it is: A DoS attack involves overwhelming a company’s server or network with traffic, rendering it inaccessible to legitimate users.
How businesses can prepare:
Traffic Analysis: Use traffic monitoring tools to identify unusual patterns that could indicate a DoS attack.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Implement CDNs to help absorb the load and mitigate the effects of traffic spikes.
Redundancy: Set up server redundancy and failover systems to maintain service availability.
5. Data Breaches
What it is: A data breach occurs when an unauthorized party gains access to a company’s sensitive data, such as customer information, intellectual property, or financial records.
How businesses can prepare:
Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit to make it unreadable in case of a breach.
Access Controls: Implement strong access controls and audit logs to detect and prevent unauthorized access.
Incident Response Plan: Have a well-defined incident response plan to quickly manage and contain data breaches.

6. Supply Chain Attacks
What it is: Supply chain attacks target third-party vendors or service providers that companies rely on, often to access the company’s network or systems indirectly.
How businesses can prepare:
Vendor Risk Management: Vet third-party vendors for cybersecurity practices and require them to meet your security standards.
Monitoring: Continuously monitor the security of third-party services and software used by your business.
Contracts: Include cybersecurity clauses in contracts with third-party vendors to hold them accountable for data protection.
7. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
What it is: APTs are long-term, targeted cyberattacks aimed at infiltrating a business’s network to steal sensitive information or disrupt operations over time.
How businesses can prepare:
Network Security: Invest in advanced network security systems such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
Employee Awareness: Ensure employees are aware of social engineering tactics commonly used in APTs.
Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about emerging cyber threats and share threat intelligence with industry peers.
8. Malware and Viruses
What it is: Malware (malicious software) includes viruses, worms, and spyware designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to systems.
How businesses can prepare:
Antivirus Software: Deploy comprehensive antivirus and anti-malware tools across all devices.
Security Updates: Keep all software and operating systems up-to-date with the latest patches to fix vulnerabilities.
Network Segmentation: Use network segmentation to limit the spread of malware.

General Best Practices for Cybersecurity Preparation:
Cybersecurity Policies: Create clear and comprehensive cybersecurity policies and ensure that all employees are familiar with them.
Incident Response Plan: Have an incident response plan in place that outlines how to handle a cyberattack, from detection to recovery.
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement.
Cyber Insurance: Consider investing in cyber insurance to help mitigate the financial impact of a cybersecurity incident.
By taking proactive steps to prepare for cybersecurity threats, businesses can reduce their risk of falling victim to cyberattacks and better protect their assets, data, and reputation.






