What policies have been successful in reducing income inequality across nations?

What policies have been successful in reducing income inequality across nations?
by Maximilian 11:28am Jan 04, 2025
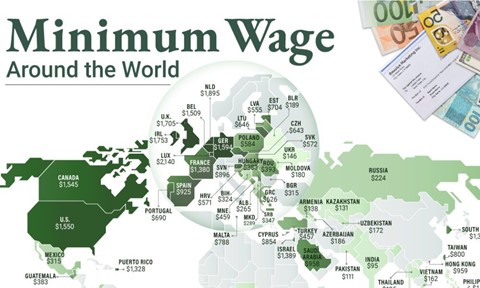
Several policies have proven effective in reducing income inequality across nations, with success varying based on context, implementation, and complementary measures. Here are key policy areas and examples of success stories:
1. Progressive Taxation
Higher Taxes on Wealth and Income: Progressive tax systems that impose higher rates on top earners reduce income disparities.
Example: Nordic Countries (Sweden, Denmark, Finland): These nations use progressive taxation to fund robust social programs, achieving some of the world's lowest levels of income inequality.
Capital Gains and Wealth Taxes: Taxing capital income and wealth can address disparities in asset ownership.
Example: France’s Solidarity Tax on Wealth (1982–2017): Although discontinued, it highlighted how wealth taxes can target extreme inequality.

2. Social Transfers and Benefits
Universal Basic Services: Providing free or subsidized healthcare, education, and childcare reduces the financial burden on low- and middle-income families.
Example: Germany: Offers universal healthcare and subsidized education, narrowing income gaps.
Unemployment Benefits and Pensions: Generous social safety nets protect vulnerable populations.
Example: Netherlands: Comprehensive unemployment insurance and pensions contribute to equitable income distribution.
3. Minimum Wage Policies
Living Wages: Establishing and regularly updating minimum wages reduces wage inequality.
Example: United Kingdom: The introduction of the National Living Wage in 2016 helped raise incomes for low-wage workers without significant employment losses.
Collective Bargaining: Strengthening labor unions ensures fair wage negotiations.
Example: Germany: Collective bargaining agreements cover a large portion of the workforce, helping reduce wage disparities.

4. Education and Skill Development
Accessible Education: Investing in free or affordable quality education promotes equal opportunities.
Example: South Korea: Heavy investment in education helped transition the economy to high-skill industries, reducing inequality over time.
Vocational Training: Skill development programs help workers access better-paying jobs.
Example: Germany: The dual education system combines apprenticeships with vocational schooling, reducing income gaps.
5. Gender Equality Measures
Equal Pay Legislation: Closing the gender pay gap addresses income inequality.
Example: Iceland: Legally requires companies to prove they provide equal pay for equal work.
Paid Parental Leave: Supports families and encourages female workforce participation.
Example: Norway: Generous parental leave policies and subsidized childcare reduce gender-based income disparities.
6. Employment and Economic Inclusion Policies
Job Creation Programs: Governments invest in sectors that create broad-based employment.
Example: China: Rapid industrialization combined with rural-to-urban migration policies significantly reduced poverty and income inequality.
Informal Sector Support: Formalizing informal employment through legal protections and benefits improves income stability.
Example: Brazil’s Bolsa Família Program: Combines conditional cash transfers with efforts to formalize employment, reducing inequality and poverty.
7. Land and Wealth Redistribution
Land Reform: Redistributing land or ensuring fair land ownership can reduce rural inequality.
Example: Taiwan: Post-WWII land reforms redistributed agricultural land, leading to more equitable economic development.
Asset-Building Programs: Encouraging savings and investment among low-income households.
Example: Singapore: The Central Provident Fund helps citizens save for retirement, healthcare, and housing, reducing wealth inequality.
8. Inclusive Economic Policies
Small Business Support: Providing microloans and grants to small enterprises fosters inclusive growth.
Example: Bangladesh’s Grameen Bank: Microfinance programs have empowered millions of low-income entrepreneurs, particularly women.
Regional Development: Investments in underserved areas reduce geographical disparities.
Example: China’s Western Development Program: Targeted investments reduced income gaps between urban coastal regions and rural interior areas.

9. Fiscal Responsibility
Efficient Use of Resources: Governments that allocate funds effectively towards social programs see better inequality outcomes.
Example: Uruguay: Progressive taxation and well-targeted social spending have successfully reduced income inequality in Latin America.
10. Global Trade and Investment Policies
Fair Trade Practices: Supporting small-scale farmers and producers through fair trade reduces global income disparities.
Example: Fairtrade Certification: Improves incomes for producers in developing countries.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Policies that channel FDI into infrastructure and job creation benefit lower-income groups.
Example: Vietnam: FDI-driven growth in manufacturing has significantly reduced poverty and income inequality.

Lessons Learned
Holistic Approaches Work Best: Combining education, taxation, and labor policies yields better results than isolated measures.
Long-Term Commitment: Sustained efforts are required for meaningful impact, as structural inequality is deeply ingrained.
Tailored Solutions: Policies must reflect local economic, cultural, and institutional contexts to be effective.






