What are the most recent scientific advancements in understanding climate systems?

What are the most recent scientific advancements in understanding climate systems?
by Maximilian 04:28pm Jan 06, 2025
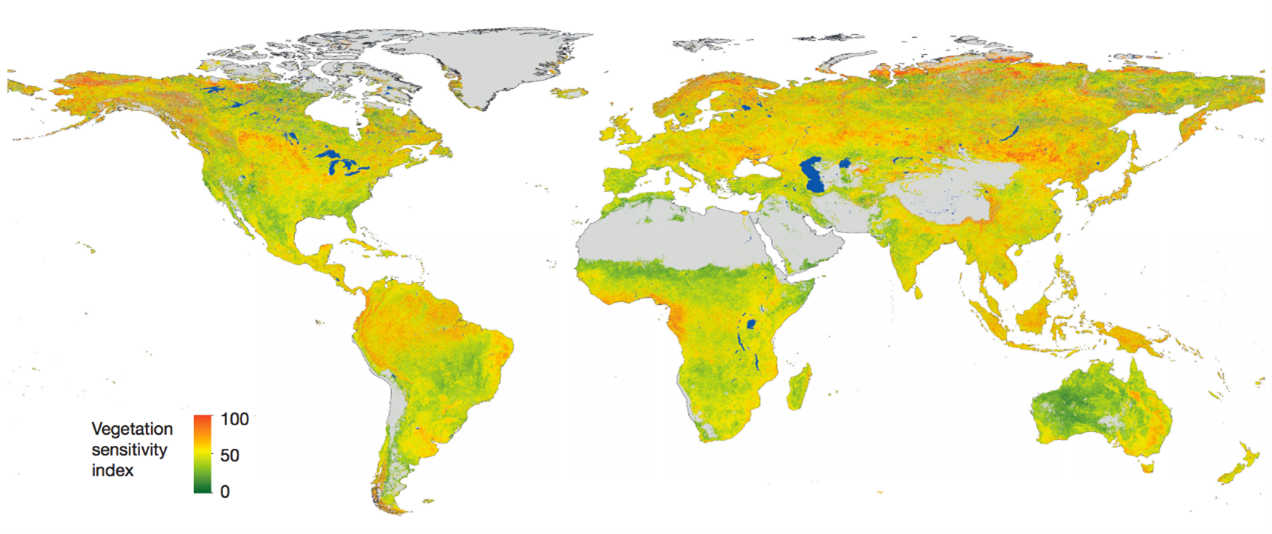
Certainly! Let’s break down some of the most recent advancements in understanding climate systems and their implications:
1. Accelerated Global Warming
Recent studies have shown that global warming is accelerating faster than previously anticipated. The current rate of warming is approximately 0.26°C per decade, which is higher than historical averages. This acceleration is a clear warning sign of the compounding effects of greenhouse gas emissions and underscores the urgency of implementing global climate policies.
Implication: Faster warming increases the likelihood of crossing climate tipping points, which are irreversible changes in the climate system, such as the melting of polar ice or the collapse of rainforests.
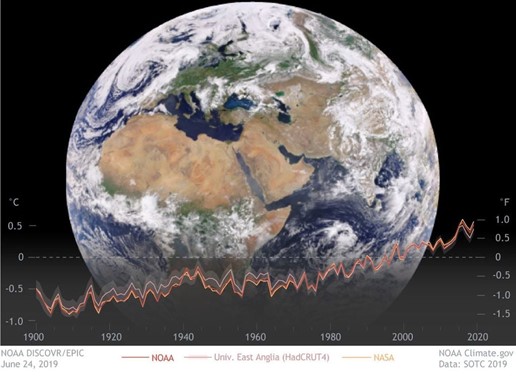
2. Enhanced Climate Modeling with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing climate modeling. They enable researchers to predict climate tipping points with greater precision. For example, AI models have improved the accuracy of predictions related to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a key ocean current system that helps regulate global climate.
Implication: Accurate predictions of tipping points allow policymakers to prepare and potentially avert catastrophic climate outcomes, such as disrupted weather patterns and rising sea levels.
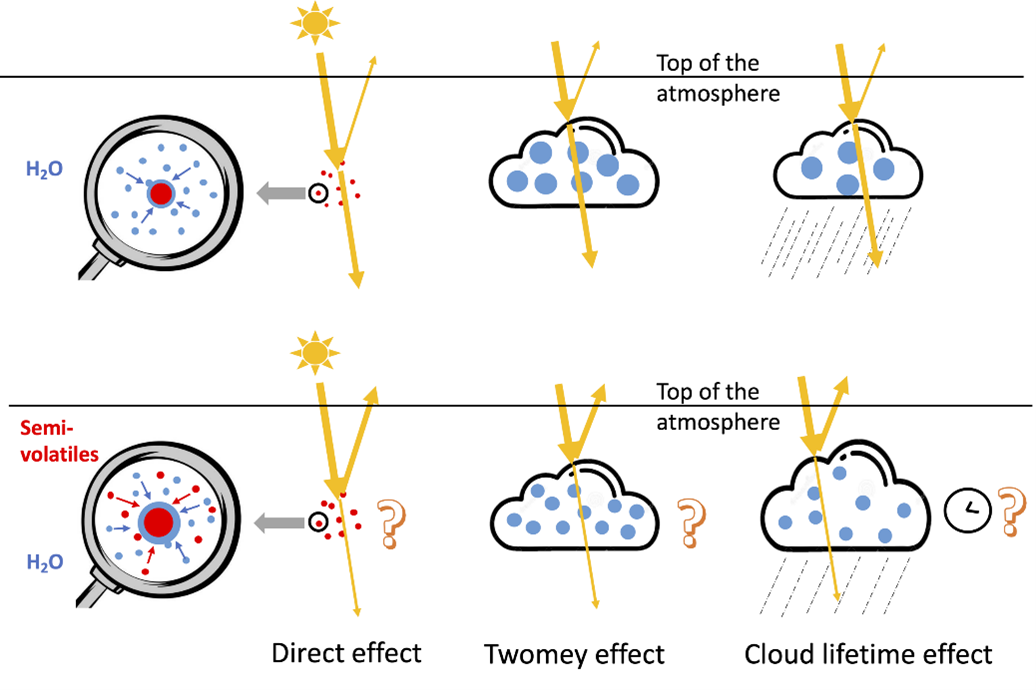
3. Understanding Aerosol-Climate Interactions
Recent findings have shown how reductions in aerosols (small particles in the atmosphere, often from pollution) reveal the true extent of warming caused by greenhouse gases. Aerosols have a cooling effect, so when air pollution decreases, the warming effect of greenhouse gases becomes more apparent.
Implication: This has revealed unexpected regional climate impacts, such as shifts in rainfall patterns and increased frequency of extreme weather events like droughts or hurricanes.
4. Advances in Attribution Science
Attribution science has advanced significantly, allowing scientists to link extreme weather events directly to human-caused climate change. For example, research has shown that climate change increased rainfall during hurricanes like Hurricane Milton by 20–30% and wind speeds by about 10%.
Implication: This evidence strengthens the case for urgent climate action and helps communities prepare for climate-induced disasters.
5. Improved Climate Sensitivity Estimates
"Climate sensitivity" refers to how much the Earth’s temperature will increase if carbon dioxide levels double. Recent advancements in modeling have refined these estimates, improving the accuracy of long-term climate projections.
Implication: Better estimates help policymakers understand the severity of potential warming scenarios and guide efforts to mitigate emissions.

Why These Advancements Matter
These breakthroughs collectively enhance our ability to predict and respond to climate change. They:
Inform international agreements like the Paris Accord.
Provide actionable insights for disaster preparedness.
Strengthen evidence linking human activities to climate change.
Understanding these systems is critical for crafting effective solutions to protect ecosystems and human societies from the worst impacts of climate change.






