How is climate change affecting agricultural productivity worldwide?

How is climate change affecting agricultural productivity worldwide?
by Maximilian 02:16pm Jan 08, 2025
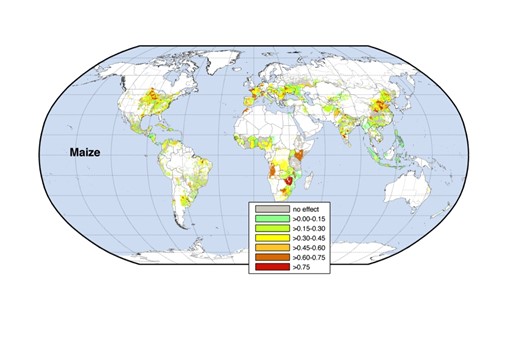
Climate change is having a profound impact on agricultural productivity worldwide, with both positive and negative effects, though the negatives often outweigh the benefits. The extent and nature of these effects vary by region, crop type, and farming practices. Here's an overview:
Negative Impacts
1. Altered Growing Conditions
Temperature Changes: Rising temperatures can shorten growing seasons, reduce crop yields, and negatively affect crops that are sensitive to heat, such as wheat, rice, and maize.
Heat Stress: High temperatures can reduce plant fertility and water-use efficiency, leading to lower productivity.
2. Water Stress
Droughts: Prolonged dry periods reduce water availability for irrigation and stress crops, leading to reduced yields.
Flooding: Intense rainfall and flooding can waterlog soils, damage crops, and disrupt planting schedules.
3. Soil Degradation
Erosion: Increased rainfall intensity and deforestation accelerate soil erosion, depleting nutrients essential for crops.
Loss of Organic Matter: Higher temperatures and erratic rainfall reduce soil organic content and fertility.
4. Pest and Disease Proliferation
Expanded Ranges: Warmer temperatures allow pests and pathogens to spread to new areas, affecting crops previously not at risk.
Increased Outbreaks: Changing weather patterns can create favorable conditions for pest and disease outbreaks.
5. Crop-Specific Impacts
Staple Crops: Major crops like maize, wheat, and rice are particularly vulnerable to heat stress, reducing yields in key growing regions.
Specialty Crops: Climate-sensitive crops like coffee, tea, and cocoa are at risk of declining productivity as their ideal growing zones shift.
6. Livestock Productivity
Heat Stress: Higher temperatures affect livestock health, reproduction, and milk/meat production.
Forage Availability: Changes in rainfall and temperature patterns reduce the quality and quantity of grazing lands.

Regional Disparities
Tropical and Subtropical Regions: These areas are disproportionately affected due to higher baseline temperatures, increased drought risk, and limited adaptive capacity.
Temperate Regions: Some temperate areas may initially benefit from longer growing seasons and milder winters, but these gains are often offset by increased weather variability and extreme events.
Positive Impacts
Longer Growing Seasons: In some colder regions, rising temperatures allow for longer growing seasons and the cultivation of new crops.
CO₂ Fertilization: Increased atmospheric CO₂ can enhance photosynthesis and water-use efficiency in some crops, though the benefits are limited and dependent on other factors like nutrient availability.
Expanded Arable Land: Warming temperatures may make some currently inhospitable areas suitable for agriculture.
Economic and Social Impacts
Food Security: Reduced agricultural productivity threatens food supply, particularly in vulnerable regions, exacerbating hunger and malnutrition.
Market Volatility: Crop failures and yield variability increase food prices and market instability.
Migration: Declining agricultural viability drives rural populations to migrate, often leading to urban overcrowding and resource strain.
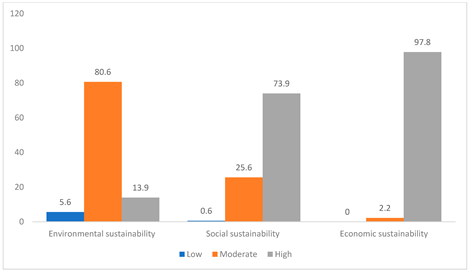
Adaptive Measures
Crop Breeding: Developing heat- and drought-resistant crop varieties can mitigate some impacts.
Improved Water Management: Techniques like drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting enhance water-use efficiency.
Agroforestry: Integrating trees with crops and livestock improves soil health and resilience to climate stress.
Climate-Smart Agriculture: Practices like crop rotation, conservation tillage, and precision farming can increase productivity and reduce emissions.
Conclusion
Climate change poses significant challenges to global agricultural productivity, with risks to food security, rural livelihoods, and economies. Proactive adaptation measures and sustainable farming practices are essential to mitigate these impacts and ensure resilience in the face of ongoing climate changes.






