The Politics of Space Exploration

The Politics of Space Exploration
by vivienne 03:35pm Jan 10, 2025

The Politics of Space Exploration is a complex and multifaceted subject that involves the intersection of science, technology, national interests, geopolitics, economics, and international relations. As humanity pushes beyond Earth, the implications of space exploration go far beyond scientific discovery, encompassing global power dynamics, economic competition, and national security. Below is an exploration of the key themes that shape the politics of space exploration today.

1. Historical Context and the Space Race
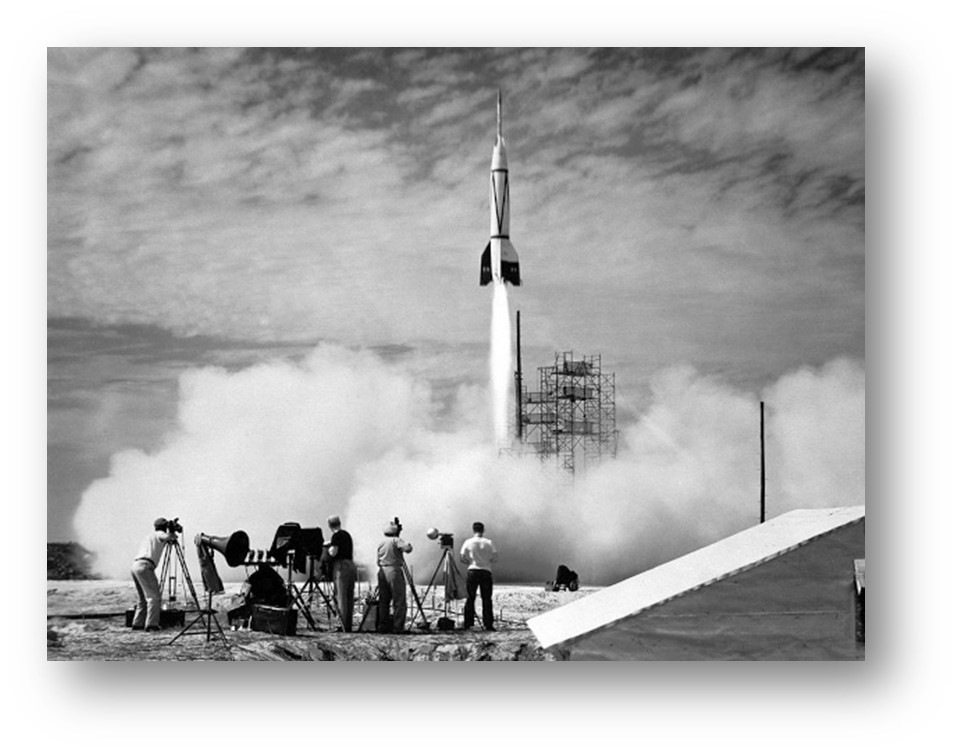

The politics of space exploration began in earnest during the Cold War with the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union. In the 1950s and 1960s, space became a key battleground for demonstrating technological superiority and ideological dominance. Milestones like the Soviet launch of Sputnik in 1957 and the American Apollo 11 moon landing in 1969 were as much about scientific achievement as they were about showcasing national prowess.
Political Motivations: Space exploration was used as a tool of soft power. Achievements in space science were symbolic of a nation’s technological capabilities and served as propaganda to boost national pride and influence global perceptions.
Military Concerns: The development of rockets for space exploration also had military applications. Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), for example, were closely related to rocket technology developed for space missions.
2. National Interests and Modern Space Programs
Today, space exploration is driven not only by scientific curiosity but also by national interests, economic ambitions, and security concerns. Countries like the United States, China, Russia, and the European Union invest heavily in space programs for several reasons:
Strategic Advantage: Dominance in space is seen as crucial for maintaining technological and military superiority. This includes developing satellite technology for communications, GPS, weather forecasting, and surveillance.
Economic Potential: There is growing interest in the economic possibilities of space, including resource extraction (e.g., mining asteroids), satellite-based internet services, and even space tourism.
Scientific Prestige: Achieving breakthroughs in space exploration can elevate a nation's global status, as seen with China's successful Change missions and Mars rover program.
3. International Cooperation vs. Competition
While space exploration has historically been competitive, it has also fostered international collaboration. Organizations like the International Space Station (ISS), a joint effort involving NASA, Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and others, exemplify how space can serve as a platform for cooperation.
Collaborative Projects: The ISS is an example of how countries with competing interests can work together to achieve scientific goals. This collaboration, however, has been tested in recent years by geopolitical tensions, such as Russia's plans to withdraw from the ISS.
Emerging Space Powers: In addition to the traditional spacefaring nations, countries like India, Israel, and the United Arab Emirates have made significant strides in space exploration, adding new players to the geopolitical landscape.
4. The Role of Private Companies
The rise of private companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and others has dramatically changed the dynamics of space exploration. These companies are pushing the boundaries of what was once solely the domain of government agencies, often more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Commercialization of Space: Companies like SpaceX have made space launches more accessible and affordable, creating new opportunities for satellite deployment, space tourism, and potential lunar and Martian exploration.
Regulatory Challenges: The involvement of private entities in space raises questions about regulation, liability, and the commercialization of space resources. There are concerns that without proper oversight, space could become the "Wild West" of the 21st century.
5. Space Treaties and Legal Frameworks
The existing international legal framework governing space is rooted in the Outer Space Treaty of 1967, which outlines several key principles:
Space is considered the "province of all mankind" and cannot be claimed by any single nation.
The use of space must be for peaceful purposes, and the deployment of nuclear weapons or other weapons of mass destruction in space is prohibited.
Nations are responsible for their activities in space, including those conducted by private companies.
However, the Outer Space Treaty is becoming outdated in light of new developments, such as plans for lunar bases, asteroid mining, and commercial space stations. The lack of clarity on property rights, resource extraction, and space traffic management poses challenges for international cooperation and governance.
6. Security Concerns and Space Militarization
The potential militarization of space is a significant concern in the politics of space exploration. With advancements in anti-satellite weapons (ASAT), satellite jamming, and space-based surveillance, nations are increasingly investing in the defense of their space assets.
Space as a Warfighting Domain: The establishment of the U.S. Space Force in 2019 underscores the recognition of space as a critical domain for national security. Other nations, such as China and Russia, are also developing capabilities to protect their interests in space.
Weaponization vs. Peaceful Use: While the Outer Space Treaty prohibits weapons of mass destruction in space, it does not explicitly ban conventional weapons. This legal gray area has led to calls for updated treaties to prevent an arms race in space.
7. Space Exploration and Environmental Concerns
As space activities increase, so do concerns about the environmental impact:
Space Debris: The accumulation of space debris, such as defunct satellites and spent rocket stages, poses a risk to satellites, space stations, and future missions. Managing this debris is becoming a priority for international space agencies.

Sustainable Space Exploration: Ensuring that future space missions are conducted sustainably is crucial to avoid depleting space resources or causing irreversible damage to extraterrestrial environments.
8. Ethics and the Future of Space Exploration
As humanity looks toward establishing a presence on the Moon, Mars, and beyond, there are ethical considerations that need to be addressed:
Exploitation vs. Stewardship: The potential extraction of resources from celestial bodies raises questions about ownership and the impact on potential extraterrestrial ecosystems.
Human Rights in Space: As private companies plan for space tourism and potentially permanent colonies, questions about labor rights, health standards, and legal jurisdiction in space are emerging.
Conclusion
The politics of space exploration reflect a delicate balance between cooperation and competition, national interests, and global aspirations. As we move deeper into the 21st century, the interplay between technological advancements, economic ambitions, international law, and geopolitical tensions will shape the future of humanity's presence beyond Earth.
In this evolving landscape, the challenge will be to ensure that space remains a realm for peaceful exploration and shared human progress, rather than becoming a new arena for conflict and exploitation.






