How effective were policy responses in mitigating the crisis

How effective were policy responses in mitigating the crisis
by Maximilian 11:51am Jan 11, 2025
The policy responses to the 2008 global financial crisis, including bailouts and stimulus packages, played a critical role in stabilizing the economy and preventing a deeper recession. However, their effectiveness varied across measures and countries, with both successes and criticisms emerging. Here's an analysis of their impact:
1. Bank Bailouts
Effectiveness:
Prevented a Financial Collapse: Bailouts for major banks and financial institutions, such as the U.S. Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), were crucial in stabilizing the banking sector. By injecting capital into failing institutions, governments prevented systemic failures.
Restored Confidence: By backing large institutions, governments reassured markets and avoided widespread panic.
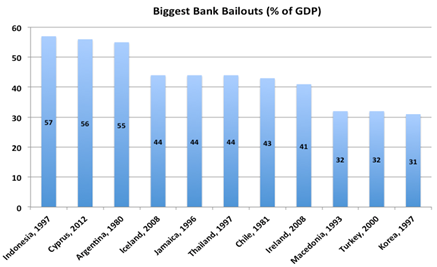
Criticisms:
Moral Hazard: Critics argue that bailouts reinforced the "too big to fail" mentality, encouraging risky behavior in the future.
Public Backlash: Taxpayer funds were used to rescue institutions seen as responsible for the crisis, leading to widespread dissatisfaction.
Limited Support for Smaller Entities: Bailouts often focused on large firms, leaving smaller businesses and individuals with less assistance.
2. Economic Stimulus Packages
Effectiveness:
Boosted Demand: Stimulus spending, such as the U.S. American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA), injected funds into infrastructure projects, education, and healthcare, supporting jobs and economic activity.
Global Coordination: Countries like China launched massive stimulus efforts that fueled global demand and trade, benefiting the wider economy.
Mitigated Unemployment: Stimulus measures helped create or save millions of jobs, reducing the severity of the economic downturn.
Criticisms:
Debt Burden: Many countries significantly increased their national debt to fund stimulus efforts, raising concerns about long-term fiscal sustainability.
Uneven Impact: Stimulus benefits were not evenly distributed across regions and demographics, with some groups experiencing limited relief.
Execution Delays: Infrastructure and public works projects often faced delays, reducing the immediate impact of the stimulus.

3. Monetary Policy
Effectiveness:
Lowered Interest Rates: Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank, slashed interest rates to near-zero levels, making borrowing cheaper and stimulating investment.
Quantitative Easing (QE): Massive asset purchase programs injected liquidity into the financial system, stabilizing credit markets and boosting confidence.
Currency Stability: Central banks coordinated efforts to ensure currency stability and prevent competitive devaluations.
Criticisms:
Wealth Inequality: QE and low interest rates disproportionately benefited asset owners, exacerbating wealth inequality.
Limited Lending to Main Street: Despite increased liquidity, banks were often hesitant to lend to small businesses and consumers, reducing the effectiveness of monetary policy for the broader economy.
4. Regulatory Reforms
Effectiveness:
Strengthened Oversight: Reforms like the Dodd-Frank Act in the U.S. imposed stricter regulations on financial institutions, reducing systemic risks.
Capital Requirements: Banks were required to hold higher capital reserves, making them more resilient to future shocks.
Consumer Protection: Measures like the creation of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) aimed to safeguard consumers from predatory practices.
Criticisms:
Complexity: Regulatory reforms were often criticized as overly complex, creating compliance challenges for smaller institutions.
Loopholes: Some argue that reforms did not address key issues, such as the shadow banking system and certain derivatives markets.
5. International Cooperation
Effectiveness:
Coordinated Efforts: The G20 and other international bodies worked together to implement synchronized policy responses, stabilizing the global economy.
Global Financial Reforms: Agreements on capital standards (e.g., Basel III) improved the resilience of the global financial system.
Criticisms:
Unequal Recovery: Developing nations faced greater challenges in implementing large-scale stimulus or bailouts, leading to slower recoveries compared to advanced economies.
Lack of Long-Term Vision: Critics argue that international cooperation focused more on immediate stabilization than addressing root causes of inequality and systemic risk.
Overall Assessment
Successes:
Averted a Great Depression: Timely and coordinated actions prevented the crisis from escalating into a full-blown global depression.
Economic Recovery: Although slow, economies began recovering by 2010, with employment and growth rates gradually improving.
Strengthened Financial Systems: Regulatory reforms and increased capital reserves reduced the likelihood of a similar crisis in the near term.
Shortcomings:
Rising Inequality: Many policy responses disproportionately benefited large corporations and wealthier individuals, leaving lower-income groups behind.
Slow Recovery for Some: Recovery was uneven, with certain sectors and regions taking much longer to rebound.
Increased Public Debt: Stimulus spending significantly increased national debt levels, leading to austerity measures in some countries, which slowed growth.






