What role do cyberattacks and digital warfare play in modern conflicts?

What role do cyberattacks and digital warfare play in modern conflicts?
by Maximilian 05:07pm Jan 02, 2025

Cyberattacks and digital warfare have become integral components of modern conflicts, with their role expanding significantly in scope, sophistication, and impact. Here's an overview of their influence:
1. Disruption of Critical Infrastructure
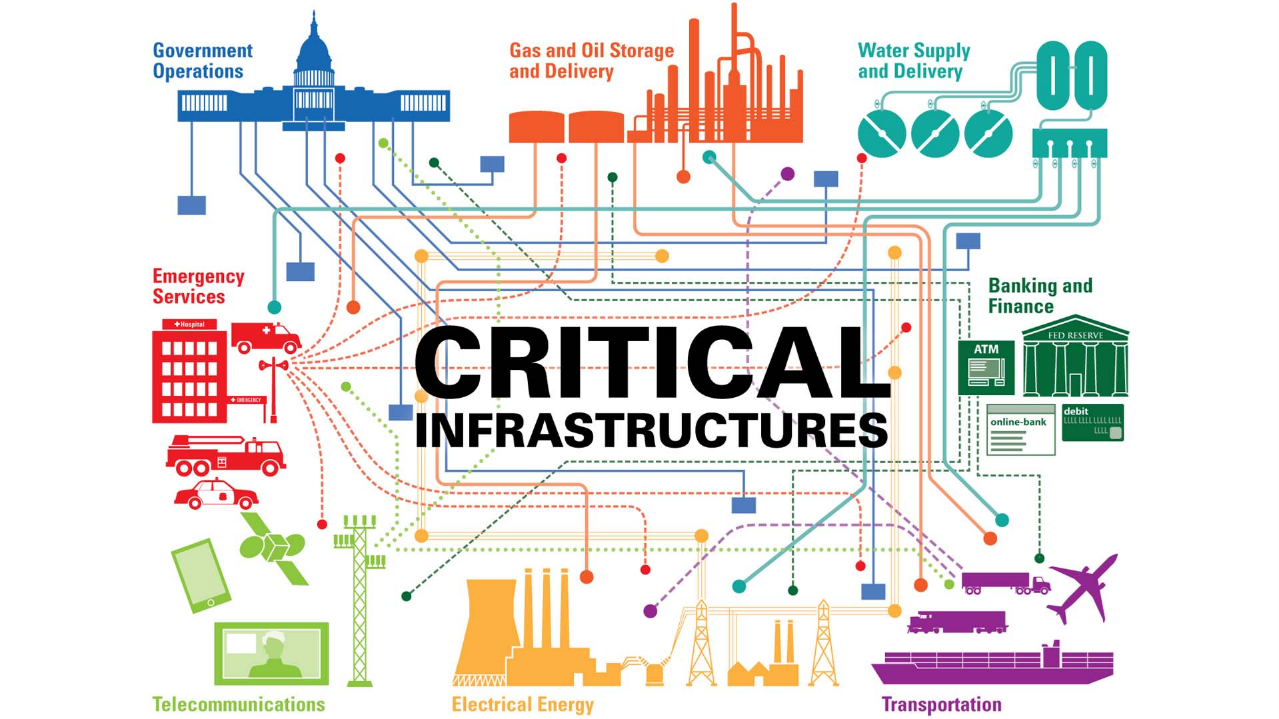
Cyberattacks target vital systems such as power grids, water supplies, transportation networks, and healthcare systems. For example, ransomware or distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks can cripple essential services, causing chaos and undermining public confidence.
Examples:The 2015 and 2016 cyberattacks on Ukraine's power grid, which caused significant blackouts.
2. Espionage and Intelligence Gathering
Digital tools enable adversaries to steal sensitive information, including military strategies, government secrets, and corporate data.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) often operate covertly for long periods, extracting valuable data without immediate detection.
Examples: The SolarWinds hack, which compromised numerous U.S. government agencies and private companies.
3. Information Warfare and Propaganda
Cyber operations often include disinformation campaigns, designed to manipulate public opinion, sow discord, and undermine trust in institutions.
Social media platforms are frequently exploited for spreading fake news, inciting unrest, or influencing elections.
Examples: Russian interference in the 2016 U.S. presidential election.

4. Economic Disruption
Attacks on financial systems, such as banks and stock exchanges, can destabilize economies and erode trust in financial institutions.
Cryptocurrency-related heists and ransom demands have added a new dimension to economic warfare.
5. Military Operations and Command Disruption
Cyberattacks can disrupt military command-and-control systems, satellite communications, and weapon systems.
Cyber capabilities are used to complement traditional military operations, providing a tactical edge by disabling enemy defenses or misdirecting forces.
6. Deterrence and Signaling
Nations use cyberattacks to send messages or demonstrate capabilities without resorting to kinetic conflict.
Examples include publicized breaches or leaks that showcase technical superiority or undermine an adversary’s credibility.
7. Non-State Actors and Asymmetric Warfare
Cyberwarfare levels the playing field, allowing smaller nations, insurgent groups, or hacktivists to challenge more powerful adversaries.
Examples: Groups like Anonymous targeting authoritarian regimes or terrorist organizations exploiting cyberspace for recruitment and coordination.
8. Blurring the Line Between War and Peace
Cyberattacks are often employed below the threshold of armed conflict, making attribution and response complex. This ambiguity challenges traditional definitions of warfare and international law.
Implications for Modern Conflicts
Attribution Challenges: Identifying perpetrators is often difficult due to the use of proxies, false flags, and anonymizing techniques.
Escalation Risks: Misinterpreted cyber actions can escalate into full-scale conflicts.
Legal and Ethical Questions: There’s an ongoing debate about the application of international law to cyberwarfare, including the laws of armed conflict.
Global Security: The interconnected nature of cyberspace means that attacks can have far-reaching and unintended consequences.
In modern conflicts, cyberwarfare acts as both a standalone domain and a complement to traditional military strategies, making it a critical factor in the geopolitical landscape.







