How do energy dependencies influence international relations?

How do energy dependencies influence international relations?
by Maximilian 03:12pm Jan 03, 2025
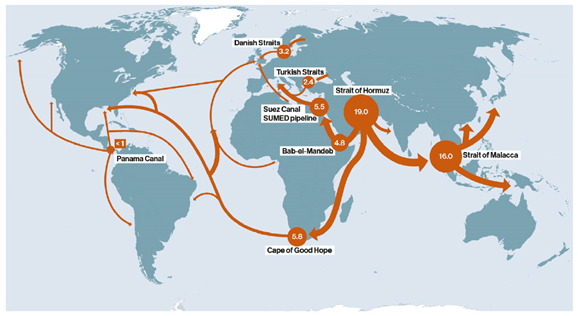
Energy dependencies play a crucial role in shaping international relations in various ways. These dependencies arise when countries rely on the energy resources (such as oil, natural gas, and electricity) of other nations to meet their energy needs. The influence of energy dependencies on international relations can be understood through several key factors:
1. Economic Leverage and Power Dynamics
Countries that are rich in energy resources (e.g., oil-rich nations in the Middle East or gas-exporting nations like Russia) can exert economic leverage over those that are dependent on energy imports. By controlling the supply of energy, these resource-rich countries can influence the economic stability, growth, and energy security of importing nations. In turn, this can translate into diplomatic and political power, as the importing nations may be compelled to align with the interests of the exporting countries, sometimes even at the cost of their own national interests or values.
2. Geopolitical Tensions and Conflicts
Energy dependencies can also be a source of tension and conflict between countries. For example, competition for access to energy resources can spark territorial disputes, military confrontations, or diplomatic stand-offs. This has been seen in cases like Russia's energy dominance over Eastern Europe and its actions in Ukraine, or the ongoing tensions between China and various countries over control of energy-rich territories in the South China Sea. Countries with high energy dependence may be vulnerable to coercion or blackmail, especially when they lack alternative energy sources or diversification.
3. Strategic Alliances and Trade Partnerships
To mitigate the risks associated with energy dependency, countries often seek to form strategic alliances and trade partnerships. These agreements can be bilateral (e.g., between energy exporters and importers) or multilateral (e.g., in the context of international organizations such as OPEC or the International Energy Agency). Countries may also invest in energy infrastructure projects, such as pipelines, oil terminals, or liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals, to diversify their energy sources and reduce vulnerabilities.
4. Energy Transition and Global Cooperation
As countries transition toward renewable energy sources (such as wind, solar, and hydropower), energy dependencies are shifting. The need for fossil fuels may decrease, changing the dynamics of global energy markets. This transition requires international cooperation to tackle climate change, create new trade flows, and reduce dependencies on polluting energy sources. Countries that are leading in renewable energy technologies, like those in Europe or North America, may strengthen their global influence through technology exports, while energy-dependent countries may face challenges in managing the energy transition.
5. Energy Security and National Strategy
Energy security is a key component of national strategy, and energy dependencies are directly linked to a country’s security policies. Nations that are highly dependent on energy imports must secure stable and reliable energy supplies through diverse sources, which can drive them to engage in multilateral negotiations or military alliances. Additionally, countries may seek to maintain strategic control over energy routes (such as sea lanes for oil shipping) or energy reserves to protect their national security interests.
6. Sanctions and Diplomatic Pressure
Energy dependencies can become a tool for sanctions and diplomatic pressure. For instance, a country with significant energy resources might impose or threaten to cut off energy supplies to punish or pressure another country into aligning with its foreign policy objectives. This was evident in Russia's use of natural gas exports to influence Europe, or the U.S. imposing sanctions on countries like Iran and Venezuela that affect their oil exports.

7. Energy Diplomacy
Many nations engage in energy diplomacy to secure long-term energy supplies and build international relations. This diplomacy often involves multilateral negotiations, energy trade agreements, and the development of energy infrastructure in countries of strategic interest. Energy diplomacy can strengthen alliances, facilitate economic development, and provide a tool for exerting influence on global politics.
In sum, energy dependencies significantly shape international relations by influencing economic, political, and security strategies. The interplay of energy needs and power can foster cooperation, but it can also lead to tension, conflict, and competition for resources. As the world shifts toward renewable energy, these dependencies may evolve, altering geopolitical and economic alignments in the future.






