How can governments and international organizations support resilience in vulnerable regions?

How can governments and international organizations support resilience in vulnerable regions?
by Nathaniel 04:58pm Jan 08, 2025
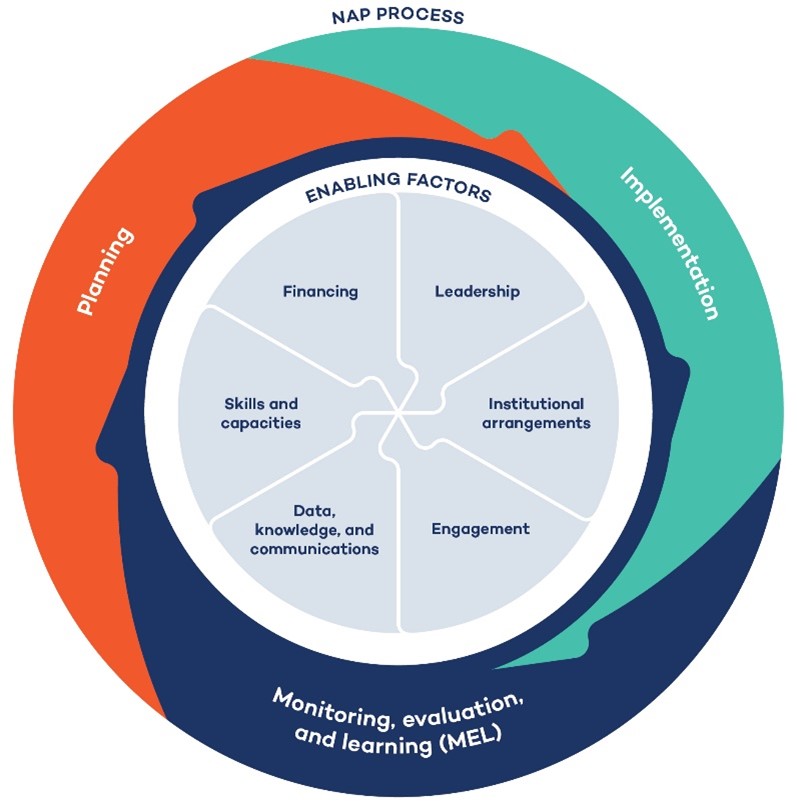
How can governments and international organizations support resilience in vulnerable regions?
Governments and international organizations play a crucial role in supporting resilience in vulnerable regions, especially in the face of climate change, natural disasters, economic challenges, and political instability. Their support can be in the form of financial assistance, technical expertise, policy frameworks, and capacity building to ensure that these regions can better withstand shocks and adapt to changing conditions. Here are some key ways in which they can help:
1. Providing Financial Support and Funding
Strategy:Governments and international organizations can provide financial assistance to vulnerable regions to fund resilience-building projects.This can include direct grants, low-interest loans, or investments in critical infrastructure and social services.
Examples:
Green Climate Fund (GCF): The GCF, established under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), offers financial assistance to developing countries to support climate resilience projects, such as flood defenses, drought mitigation, and sustainable agriculture practices.
World Bank's Climate Investment Funds: These funds provide financial resources for countries and regions to implement climate adaptation strategies, including water management systems and climate-resilient infrastructure.
Effectiveness:Financial support enables vulnerable regions to access the resources needed to enhance resilience, particularly in areas that lack the capacity to fund such projects independently.
2. Capacity Building and Technical Assistance
Strategy:International organizations and national governments can offer training, education, and knowledge-sharing programs to strengthen local capacities.This includes building skills in disaster management, sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, and climate science.
Examples:
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): The UNDP helps vulnerable countries build their capacity to address climate change through programs such as disaster risk reduction and sustainable development initiatives.
The World Bank: In partnership with national governments, the World Bank offers technical assistance to improve resilience, such as in the construction of flood-resistant infrastructure or strengthening early warning systems for extreme weather events.
Effectiveness:Capacity building helps local authorities and communities take ownership of resilience-building efforts and ensures that adaptation measures are sustainable in the long term.
3. Strengthening Early Warning Systems and Disaster Preparedness
Strategy: Governments and international organizations can invest in developing and maintaining early warning systems to help vulnerable regions predict and prepare for extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
Examples:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO): The WMO works with countries to develop regional and national early warning systems that use advanced technology to forecast extreme weather events.

Regional Climate Centers (RCCs): The RCCs, supported by international organizations, assist vulnerable regions in monitoring and responding to climate-related risks by providing localized weather forecasts and early warning alerts.
Effectiveness: Early warning systems allow communities to take proactive steps to reduce damage and loss of life, and improve the overall preparedness of vulnerable regions.
4. Promoting Resilient Infrastructure Development
Strategy:Governments and international organizations can invest in resilient infrastructure to protect vulnerable communities from the impacts of climate change and natural disasters. This includes building flood defenses, strengthening transport networks, and upgrading energy systems to withstand climate impacts.
Examples:
Resilient Infrastructure for Development (RID) Program: This World Bank program helps countries design infrastructure projects that are climate-resilient, including roads, bridges, and energy grids, that can cope with changing weather patterns and extreme events.
The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB): AIIB provides financial support for infrastructure projects, including climate-resilient water management systems and renewable energy infrastructure, in vulnerable regions.
Effectiveness:Resilient infrastructure reduces vulnerability to climate impacts, helps communities recover from disasters more quickly, and contributes to long-term economic stability.
5. Strengthening Social Protection Systems
Strategy:Governments, often with the support of international organizations, can establish and expand social protection programs to reduce the vulnerabilities of the most at-risk populations, including cash transfer programs, insurance, and safety nets for communities impacted by climate disasters or economic shocks.
Examples:
The African Risk Capacity (ARC): ARC, backed by the African Union and international partners, offers insurance solutions to help African countries respond to climate-related disasters, such as droughts and floods, through timely financial payouts.
Social Protection Programs in Latin America: The "Conditional Cash Transfer" programs,such as Brazil’s Bolsa Família, provide financial assistance to low-income families and can be adapted to climate-related shocks, helping to protect vulnerable populations.
Effectiveness:Social protection systems help vulnerable communities recover from shocks, ensure basic livelihoods, and enhance resilience in the face of changing environmental and economic conditions.
6. Facilitating Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation Policies
Strategy:Governments and international organizations can support the development of policies that focus on long-term climate resilience, such as integrating climate adaptation into national development plans, adopting climate-resilient agricultural practices, and incentivizing green energy solutions.
Examples:

National Adaptation Plans (NAPs): Supported by the UNFCCC, countries can develop NAPs that lay out strategies for adapting to climate impacts, ensuring that climate resilience is integrated into national development agendas.
The EU’s Climate Adaptation Strategy: The European Union’s strategy provides funding and policy guidance for vulnerable countries, helping them to adopt sustainable, climate-resilient agriculture, urban development, and disaster management policies.
Effectiveness:Policy frameworks that integrate climate resilience ensure that climate considerations are embedded in governance and development, fostering a coordinated and long-term approach to adaptation.
7. Encouraging International Cooperation and Knowledge Sharing
Strategy:International organizations can foster collaboration between nations to share best practices, technology, and knowledge in areas such as disaster risk reduction, renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and climate-resilient infrastructure.
Examples:
The UN’s Global Platform for Disaster Risk Reduction: This platform facilitates the exchange of knowledge and experiences between governments, international organizations, and the private sector on reducing disaster risks and enhancing resilience.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): The IPCC provides a scientific basis for understanding climate change impacts and adaptation strategies, encouraging international cooperation and coordinated climate action.

Effectiveness:International cooperation accelerates the exchange of innovative solutions and helps countries that lack resources or expertise to learn from more resilient regions.
8. Addressing Vulnerable Populations and Social Inequities
Strategy: Targeting assistance to the most vulnerable populations, including women, children, indigenous communities, and marginalized groups, is key to ensuring that resilience-building efforts are inclusive and equitable.This requires tailored approaches that account for social vulnerabilities and gender inequalities.
Examples:
The Gender-Responsive Climate Change Adaptation Programme: This initiative by the UN Women and UNDP supports vulnerable communities, particularly women, in developing climate-resilient livelihoods and advocating for equal participation in climate decision-making.
Indigenous Knowledge Integration: Organizations like the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) work with indigenous populations to integrate traditional knowledge into climate adaptation strategies,empowering these communities and enhancing resilience.
Effectiveness:Addressing social inequities ensures that resilience-building is holistic, protecting those who are most at risk of climate impacts and promoting inclusive growth.
9. Promoting Sustainable and Climate-Resilient Livelihoods
Strategy:Governments and international organizations can support the development of sustainable livelihoods that are less vulnerable to climate change, including promoting green jobs, sustainable agriculture, and eco-tourism.
Examples:
Sustainable Livelihoods Programme by UNDP: This program helps communities transition from climate-sensitive industries to more sustainable and diversified livelihoods, fostering long-term resilience.
Green Jobs in Renewable Energy: Organizations like the International Labour Organization (ILO) work with governments to develop green jobs in sectors such as solar energy, sustainable agriculture, and climate-resilient construction.
Effectiveness:Promoting diverse, sustainable livelihoods helps vulnerable communities reduce their dependence on climate-sensitive activities, making them more resilient to changes in weather patterns and market shifts.






