 What Are the Best Study Hacks for Students?
What Are the Best Study Hacks for Students?
Studying effectively is a key factor in academic success, and with the right strategies, students can learn more efficiently and retain information longer.
 What Are the Must-Have Apps for Smart Travel Planning?
What Are the Must-Have Apps for Smart Travel Planning?
When it comes to smart travel planning, the right apps can help streamline your journey, ensure you get the best deals, and enhance your experience on the go.
 What were the primary causes of the 2008 global financial crisis?
What were the primary causes of the 2008 global financial crisis?
The 2008 global financial crisis (GFC) was caused by a combination of factors that interacted in complex ways
 What role do multinational corporations play in fostering or hindering economic development?
What role do multinational corporations play in fostering or hindering economic development?
Multinational corporations (MNCs) play a dual role in economic development, offering both opportunities and challenges
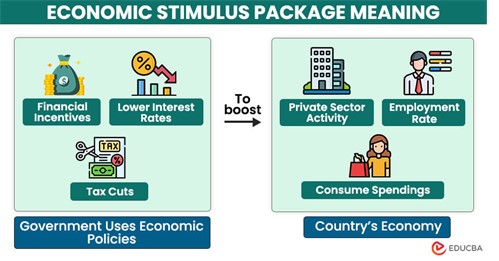 How effective were policy responses in mitigating the crisis
How effective were policy responses in mitigating the crisis
The policy responses to the 2008 global financial crisis, including bailouts and stimulus packages, played a critical role in stabilizing the economy and preventing a deeper recession
 What Makes Certain Books Timeless Classics?
What Makes Certain Books Timeless Classics?
Books become timeless classics when they transcend their time and place of origin to resonate with readers across generations
 How Has Social Media Influenced Modern Culture?
How Has Social Media Influenced Modern Culture?
Social media has profoundly influenced modern culture in a variety of ways, reshaping communication, self-expression, and societal norms
 How has globalization contributed to economic growth in developing nations?
How has globalization contributed to economic growth in developing nations?
Globalization has played a pivotal role in driving economic growth in developing nations by fostering increased connectivity, trade, and investment
 Can lessons from past financial crises prevent future ones?
Can lessons from past financial crises prevent future ones?
Lessons from past financial crises can certainly help prevent or mitigate the impact of future crises, but the complex and evolving nature of global financial systems makes it unlikely that any set of measures will completely prevent financial instability. Nevertheless, by analyzing previous crises, policymakers, regulators, and financial institutions can implement strategies that reduce risks, improve resilience, and make the financial system more robust
 Are there ways to minimize the negative effects of globalization on income inequality?
Are there ways to minimize the negative effects of globalization on income inequality?
Yes, there are several strategies that governments, organizations, and international institutions can adopt to minimize the negative effects of globalization on income inequality. These approaches focus on fostering inclusive growth, protecting vulnerable populations, and ensuring equitable distribution of the benefits of globalization
 Causes and consequences of the increase in extreme weather events
Causes and consequences of the increase in extreme weather events
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, floods, wildfires, and severe storms, have become more frequent and intense in recent years.
 The Politics of Space Exploration
The Politics of Space Exploration
The Politics of Space Exploration is a complex and multifaceted subject that involves the intersection of science, technology, national interests, geopolitics, economics, and international relations. As humanity pushes beyond Earth, the implications of space exploration go far beyond scientific discovery, encompassing global power dynamics, economic competition, and national security.
 Ambient Intelligence (AMI) and Human-Centric Computing
Ambient Intelligence (AMI) and Human-Centric Computing
As digital technology advances, there is a growing trend toward creating environments that can sense, adapt, and respond to human needs seamlessly. Ambient Intelligence (AMI) and Human-Centric Computing are two concepts at the forefront of this trend, aiming to create personalized, context-aware systems that prioritize user comfort, convenience, and empowerment.
 Biometric Authentication and Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
Biometric Authentication and Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
As digital interactions and transactions proliferate, the demand for secure, seamless authentication has grown. Biometric authentication, which uses unique biological traits (such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans) for identity verification, has become an increasingly popular solution.
 What sustainable farming practices can help mitigate climate risks?
What sustainable farming practices can help mitigate climate risks?
Sustainable farming practices are essential for mitigating climate risks while maintaining agricultural productivity. These practices reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance soil health, conserve water, and improve ecosystem resilience
 What are the long-term consequences of melting ice caps and rising sea levels?
What are the long-term consequences of melting ice caps and rising sea levels?
The long-term consequences of melting ice caps and rising sea levels are far-reaching and can significantly impact both natural ecosystems and human societies. These changes are driven by global warming and are expected to continue for centuries
 What are the challenges and benefits of achieving net-zero carbon goals?
What are the challenges and benefits of achieving net-zero carbon goals?
Achieving net-zero carbon goals presents a mix of challenges and benefits, encompassing environmental, economic, social, and technological aspects
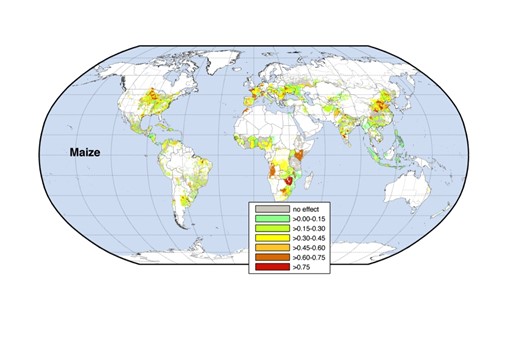 How is climate change affecting agricultural productivity worldwide?
How is climate change affecting agricultural productivity worldwide?
Climate change is having a profound impact on agricultural productivity worldwide, with both positive and negative effects, though the negatives often outweigh the benefits. The extent and nature of these effects vary by region, crop type, and farming practices

