 What progress has been made in achieving gender parity in political leadership?
What progress has been made in achieving gender parity in political leadership?
Progress toward achieving gender parity in political leadership has been uneven across the globe, but there has been significant momentum over recent decades. Various countries and regions have implemented measures to address gender imbalances in political representation, and some have seen notable advances.
 What political challenges accompany the transition to renewable energy?
What political challenges accompany the transition to renewable energy?
The transition to renewable energy presents several political challenges, as it involves profound changes to existing energy systems, economies, and international relations. These challenges affect governments, industries, and societies at both the national and global levels.
 What are the political and economic implications of large-scale migration?
What are the political and economic implications of large-scale migration?
Large-scale migration has profound political and economic implications, influencing domestic and international policies, social cohesion, and economic performance.
 How do regional alliances, like the EU or ASEAN, complement or compete with global institutions?
How do regional alliances, like the EU or ASEAN, complement or compete with global institutions?
Regional alliances such as the European Union (EU) or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) both complement and, at times, compete with global institutions like the United Nations (UN), World Trade Organization (WTO), or the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
 How do political narratives shape public attitudes toward immigration?
How do political narratives shape public attitudes toward immigration?
Political narratives significantly shape public attitudes toward immigration by framing the issue in ways that evoke emotional, cultural, or economic concerns. These narratives influence perceptions, often creating simplified or polarized views of complex realities
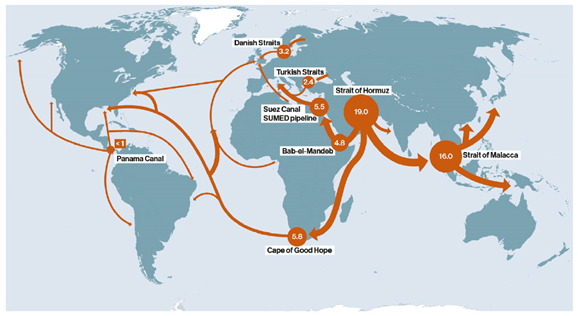 How do energy dependencies influence international relations?
How do energy dependencies influence international relations?
Energy dependencies play a crucial role in shaping international relations in various ways. These dependencies arise when countries rely on the energy resources (such as oil, natural gas, and electricity) of other nations to meet their energy needs.
 How do disputes over natural resources affect global stability?
How do disputes over natural resources affect global stability?
Disputes over natural resources—such as water, fossil fuels, minerals, and arable land—can profoundly affect global stability by fueling conflicts, disrupting economies, and straining diplomatic relationships.
 How can nations balance border security with humanitarian responsibilities?
How can nations balance border security with humanitarian responsibilities?
Balancing border security with humanitarian responsibilities is a complex challenge that requires nations to address security concerns while upholding human rights and international obligations. This balance can be achieved through a combination of legal frameworks, effective policies, and international cooperation.
 Are organizations like the United Nations and NATO still effective in maintaining global order?
Are organizations like the United Nations and NATO still effective in maintaining global order?
The effectiveness of organizations like the United Nations (UN) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in maintaining global order is a complex and often debated topic. Their relevance and impact depend on the context and the specific challenges they are addressing.
 What role do cyberattacks and digital warfare play in modern conflicts?
What role do cyberattacks and digital warfare play in modern conflicts?
Cyberattacks and digital warfare have become integral components of modern conflicts, with their role expanding significantly in scope, sophistication, and impact. Here's an overview of their influence
 What challenges do smaller nations face in navigating the influence of superpowers?
What challenges do smaller nations face in navigating the influence of superpowers?
Smaller nations face a variety of challenges when navigating the influence of superpowers in a world where major powers often seek to expand their influence.
 What are the long-term implications of populist movements on democratic institutions?
What are the long-term implications of populist movements on democratic institutions?
Populist movements can have profound long-term implications on democratic institutions, with both potential benefits and significant risks. While some populist movements address genuine grievances and bring attention to neglected issues, they often challenge the norms, structures, and principles that underpin liberal democracy.
 Is a multipolar world order better for global stability than a unipolar one?
Is a multipolar world order better for global stability than a unipolar one?
The question of whether a multipolar or unipolar world order is better for global stability is complex and has been widely debated among scholars, policymakers, and analysts. Each system has its advantages and challenges, and their relative benefits depend on the context in which they operate.
 How do populist leaders impact foreign relations and global cooperation?
How do populist leaders impact foreign relations and global cooperation?
Populist leaders can significantly impact foreign relations and global cooperation, often reshaping their country's role on the international stage. Their approach typically emphasizes nationalism, sovereignty, and a rejection of global norms, which can lead to both short-term and long-term consequences for global governance.
 How are social media platforms influencing political campaigns and public opinion?
How are social media platforms influencing political campaigns and public opinion?
Social media platforms have profoundly transformed political campaigns and public opinion by reshaping how information is disseminated, consumed, and acted upon.
 Can technology foster greater transparency in government, or does it lead to more surveillance?
Can technology foster greater transparency in government, or does it lead to more surveillance?
Technology has the potential to both foster greater transparency in government and increase surveillance, depending on how it is used and the policies in place.
 Why has populism gained momentum in various parts of the world?
Why has populism gained momentum in various parts of the world?
Populism has gained momentum in many parts of the world due to a convergence of political, economic, social, and cultural factors.

