How P2E Games Work In-game economics and tokenomics?

How P2E Games Work In-game economics and tokenomics?
by Maximilian 03:16pm Jan 10, 2025

Play-to-Earn (P2E) games combine gaming and blockchain technology to allow players to earn real-world value through in-game activities. The core of P2E games lies in their in-game economics and tokenomics, which are structured to incentivize participation and create sustainable ecosystems. Here's an overview of how they work:
1. In-Game Economics
Core Components
Game Currency: Most P2E games have an in-game currency that players earn by completing tasks, winning battles, or achieving milestones. This currency is often blockchain-based and tradable for real-world money.
Assets: Players can own unique digital assets like characters, weapons, skins, or land, represented as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). These assets can be traded or sold.
Marketplaces: Players buy, sell, and trade in-game assets in decentralized or centralized marketplaces, driving the game’s economy.
Economic Design
Earning Mechanisms: Players earn through gameplay, staking tokens, participating in governance, or other in-game activities.
Burn Mechanisms: To maintain value, games often include burning mechanisms where tokens are removed from circulation (e.g., through fees or upgrades).
Incentive Loops: Developers create incentives for continued play, such as introducing new challenges or updates.
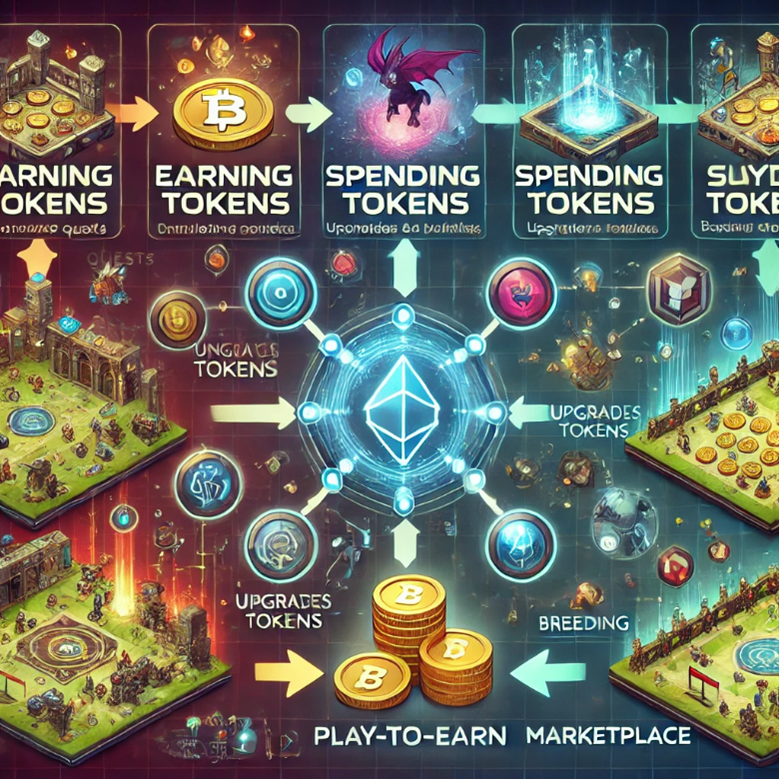
2. Tokenomics
Tokenomics refers to the design and structure of a game's tokens. These are often central to a P2E game’s economy.
Types of Tokens
Utility Tokens: Used for in-game transactions like purchasing assets, upgrades, or paying fees.
Example: SLP (Smooth Love Potion) in Axie Infinity.
Governance Tokens: Allow players to vote on game updates, economic changes, or development decisions.
Example: AXS (Axie Infinity Shards).
Reward Tokens: Distributed as rewards for gameplay or contributions to the ecosystem.
Initial Supply: Tokens are pre-minted and allocated for various purposes like rewards, development, and marketing.
Emission Schedule: Defines how new tokens enter circulation (e.g., through staking or rewards).
Cap or Inflation: Some games set a maximum supply, while others allow controlled inflation to ensure long-term sustainability.
Earning Real-World Value: Tokens can often be traded on crypto exchanges for other cryptocurrencies or fiat money.
Asset Liquidity: NFTs provide liquidity to in-game items, allowing players to monetize their gaming time.
Dual Token Systems: Separate governance and utility tokens to manage inflation.
Dynamic Rewards: Adjusting rewards based on player activity or market conditions.
Sink Mechanisms: Creating ways for players to spend tokens (e.g., upgrades, fees, or new features) to reduce circulating supply.
Player Retention: Ensuring that players stay engaged without relying solely on earning potential.
Speculation: Preve nting the economy from becoming dominated by investors rather than players.
Economic Shocks: Protecting against crashes caused by token price volatility.
Distribution and Supply
Utility and Value
3. Balancing the Economy
A successful P2E game requires a balanced economy to avoid inflation or player dissatisfaction. Common strategies include:
4. Sustainability Challenges

P2E games blend traditional gaming mechanics with blockchain technology to create interactive economies. Their success hinges on a carefully designed economic system that balances player incentives, token utility, and long-term sustainability.