The environmental impact of blockchain and P2E games

The environmental impact of blockchain and P2E games
by Maximilian 02:17pm Jan 14, 2025

The environmental impact of blockchain technology, particularly in Play-to-Earn (P2E) games, has become an increasingly important topic of discussion. While blockchain offers many benefits—such as decentralization, transparency, and enabling digital ownership—it also comes with significant environmental costs, particularly related to energy consumption. Let’s explore the environmental implications of blockchain in P2E games and potential solutions to mitigate these impacts.
Environmental Impact of Blockchain in P2E Games
1. Energy Consumption and Proof-of-Work (PoW) Blockchains
High Energy Usage: Many popular blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum (before its transition to Ethereum 2.0), rely on a consensus mechanism known as Proof-of-Work (PoW). PoW requires miners to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and secure the network. This process is energy-intensive, requiring substantial computational power and, in turn, significant electricity consumption.
Impact on Carbon Footprint: The carbon footprint of PoW blockchains is substantial, particularly when the mining is powered by non-renewable energy sources. For instance, Bitcoin mining, which operates on PoW, is often associated with high energy consumption and carbon emissions, contributing to environmental concerns.
Example: A study from Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance in 2021 found that Bitcoin’s annual energy consumption was comparable to that of entire countries, such as Argentina or the Netherlands.
Impact on P2E Games: P2E games that are built on PoW blockchains also face the same environmental challenges. Games like Axie Infinity and Decentraland, which use blockchain networks that may rely on PoW (though this has been shifting), contribute indirectly to energy consumption through transaction fees and the minting/trading of NFTs and in-game assets.

2. Transaction Fees and Network Congestion
Scalability Issues and Fees: The energy cost of processing transactions on PoW-based networks like Ethereum can increase during periods of high demand. When many players are interacting with the game and making transactions, the network can become congested, resulting in higher gas fees (transaction fees). This not only impacts the player experience but also exacerbates the environmental cost as more energy is used to process transactions.
Environmental Costs of NFTs: NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), which are integral to many P2E games, often require multiple transactions on the blockchain (e.g., for minting, trading, or transferring ownership). The creation, buying, and selling of NFTs on energy-intensive blockchains can lead to significant carbon emissions.
Solutions to Mitigate Environmental Impact
1. Transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) and Energy-Efficient Protocols
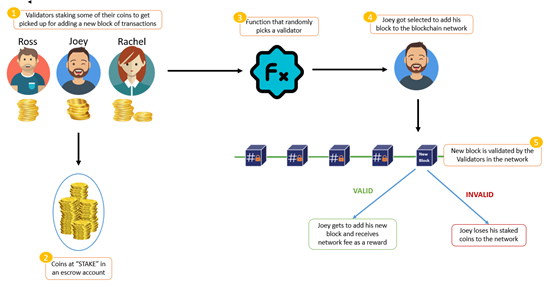
Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Many blockchains are transitioning from PoW to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), a consensus mechanism that is far more energy-efficient. PoS does not require energy-intensive mining; instead, validators are chosen to create blocks and confirm transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" as collateral. This system uses far less computational power and significantly reduces the environmental footprint of blockchain operations.
Ethereum 2.0: Ethereum, one of the largest blockchain networks used by many P2E games, has been transitioning to Ethereum 2.0, which operates on PoS. This shift is expected to drastically reduce its energy consumption, with estimates suggesting that Ethereum's energy consumption could decrease by over 99% once the full transition is complete.
Other Energy-Efficient Blockchains: In addition to Ethereum 2.0, there are blockchain platforms designed from the start with energy efficiency in mind. Solana, Tezos, and Flow are examples of blockchains that use PoS or other more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms. These networks offer faster, cheaper, and less energy-intensive alternatives for developers building P2E games and NFTs.
2. Layer-2 Solutions and Sidechains
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions: Layer-2 solutions are built on top of existing blockchains (e.g., Ethereum) to help alleviate congestion and reduce the environmental impact. By handling transactions off-chain or in a more energy-efficient manner, Layer-2 solutions reduce the number of mainchain transactions, cutting down on energy usage.
Examples of Layer-2 solutions include Polygon (for Ethereum) and Optimism, which offer faster transactions with lower energy costs while maintaining the security of the main blockchain.
Sidechains: Sidechains are independent blockchains that run parallel to the main blockchain and are designed to handle specific tasks or applications. They offer the benefit of reducing congestion on the main network and can be optimized for efficiency. Sidechains such as Polygon or xDai are used in many P2E games to lower costs and energy usage.
3. Carbon Offsetting and Green Initiatives
Carbon Offsetting Programs: Many projects in the blockchain space have started to adopt carbon offsetting practices to neutralize the environmental impact of their operations. This involves investing in projects that reduce or remove carbon emissions, such as reforestation projects or renewable energy investments.
Partnerships with Sustainability Projects: Some blockchain projects and P2E games are forming partnerships with environmental organizations to support sustainability initiatives. For instance, Flow, which is used by NBA Top Shot, has committed to being carbon-neutral by offsetting emissions produced by the network.
Green Blockchain Initiatives: Several blockchain networks are actively focusing on environmental sustainability. The Energy Web Foundation, for example, is working on using blockchain to facilitate the transition to a low-carbon energy future.
The Future Outlook for Blockchain and P2E Games
The environmental impact of blockchain technology in P2E games remains a significant concern, but there are encouraging signs that the industry is moving towards solutions that reduce its carbon footprint. The transition to Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanisms, the development of Layer-2 solutions, and the adoption of carbon offsetting strategies are all steps in the right direction. Moreover, as blockchain networks like Ethereum 2.0 and other energy-efficient platforms continue to gain traction, the environmental burden of P2E games should decrease.
As an investor or developer in the P2E space, it’s important to be aware of the environmental impact of the technologies used and to consider the long-term sustainability of the platform you are engaging with. By prioritizing energy-efficient blockchain solutions and supporting green initiatives, the P2E industry can play a role in shaping a more sustainable and eco-friendly digital economy.

Key Takeaways:
PoW blockchains (like Ethereum 1.0) contribute significantly to energy consumption and carbon emissions, which affects P2E games relying on them.
Proof-of-Stake and energy-efficient blockchains (e.g., Solana, Flow, Ethereum 2.0) provide more sustainable alternatives for P2E games.
Layer-2 solutions and sidechains can help reduce congestion and energy consumption by offloading transactions.
Carbon offsetting programs and renewable energy use are emerging as ways to mitigate the environmental impact of blockchain and NFTs in P2E games.
While the environmental impact of P2E games remains a concern, the industry's ongoing shift toward greener technologies and practices offers hope for a more sustainable future.